被动收集的信息可能不是最新的信息,通过主动的手段去发现更精确的信息
- 直接与目标系统交互通信
- 无法避免留下访问的痕迹(如果目标系统有完善的系统日志)
- 使用受控的第三方电脑进行探测
- 使用代理或已经被控制的主机
- 做好本封杀的准备
- 使用噪声迷惑目标,淹没真实的探测流量
- 扫描
- 发送不同的探测,根据返回结果判断目标状态(ip,端口,服务)
发现
- 识别活着的主机
- 潜在的被攻击目标
- 输出一个ip地址列表
- 2,3,4层发现
发现——二层发现
- 优点:扫描速度快,可靠
- 缺点:不可路由,只能发现本网段
- ARP协议
- 抓包
arping:(二层中单个存活主机的探测)
arping 192.168.0.1 -c 1``` -c是指定发送一个包以后看是否存在,否则会一直发包;如果不在一个网络里,发包的话是不存在的 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82- ```sudo arping 192.168.0.1 -d``` -d是同一个ip拥有不同的Mac地址,就是说,如果结果显示有两个Mac地址声称自己是网关,那么你的网络就存在arp欺骗,然后根据路由器查arp表进行定位
- ```sudo arping 192.168.0.1 -c 1 | grep "bytes from" | cut -d" " -f 5 |cut -d "(" -f 2 | cut -d")" -f 1``` 通过管道显示活着的主机
- 但是这样只能扫描一个ip,不能自动化的去扫描一个网段,所以用脚本去实现:扫描的时候可以指定网卡,这里用bash脚本来实现这个功能```sudo ./arping1.sh eth0 > addr.txt``` 
- 第二个脚本:这个脚本的功能是去探测已知ip列表的主机是否存活的脚本,前提是要有一个ip列表的文件```sudo ./arping2.sh addr.txt``` 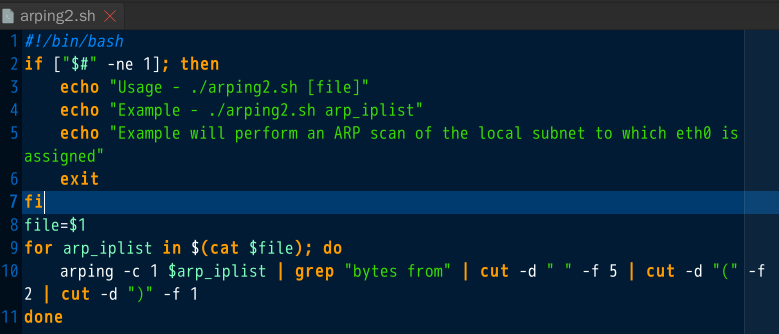
- 如果要在扫描的时候直接将结果重定向到一个文本文件中,直接早bash脚本中添加即可
2. 二层发现——nmap:
- ```nmap -sn 192.168.0.1/24``` 扫描速度更快,显示的信息更多
- > Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.1
> Host is up (0.020s latency).
> Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.101
> Host is up (0.0011s latency).
> Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.104
> Host is up (0.084s latency).
> Nmap scan report for 192.168.0.107
> Host is up (0.00059s latency).
> Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (4 hosts up) scanned in 5.65 seconds
- ```nmap -iL filename -sn``` 这个可以做和arping第二个脚本一样的工作
> -sn 参数不做端口扫描,但它不仅仅发ARP记录,还会DNS做ptr反向域名解析的解析
3. 二层发现———Netdiscover
- 专用与二层发现
- 可用于无线和交换网络环境
- 主动和被动扫描
- 主动
- netdiscover -i eth0 -r 192.168.0.1/24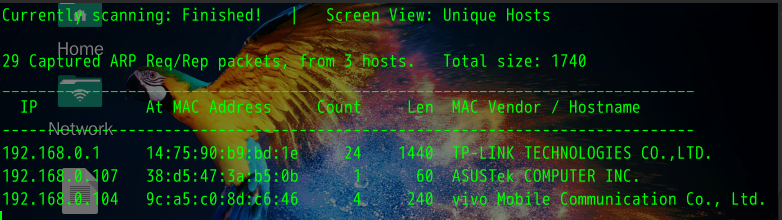
- netdiscover -l iplist.txt
- 被动
- netdiscover -p (开启混杂模式)只要在在网卡上有arp包数据,就可以侦听到: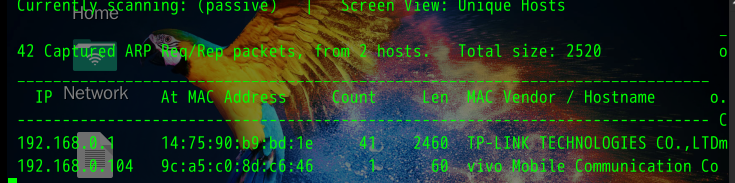
- 主动arp容易触发预警
4. 二层发现———Scapy
- scapy
- 作为Python的库文件进行调用
- 也可以做单独的工具使用
- 抓包,分析,创建,修改,注入网络流量
- apt-get install python-gnuplot
- 输入scapy启动scapy启动,然后输入ARP()调用这个函数,```ARP().display()查询ARP函数的属性``` ,这样就可以定制(arp的报头结构,将函数的属性字段添加进去,这样就可以实现一个arp查询)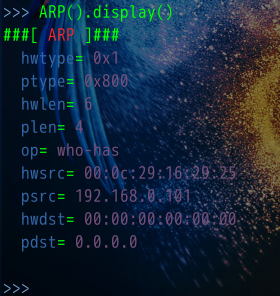
- 直接利用scapy进行arp探测,实际上就是通过调用scapy自带的函数进行查询:
- 首先```sudo scapy``` 启动进行scapy命令行模式下
- 通过```ARP().display()``` 可以查看APR这个函数下的函数头,然后这只pdst这个要查询的目标```arp.pdst="192.168.0.1"``` 这里的arp是设置的变量
- 通过```sr1(arp)``` 进行发包然后查看回显:这里也可以设置一个anwser变量带代替返回的数据包,然后调用display方法查看数据包的返回情况(有一个问题,如果查询的是一个不存在的ip,这样会一直发包,所以要加上timeout,加上一个verbose=1,显示详细的信息)
- scapy是Python的库,所以也支持Python脚本来进行探测,可以调用这个库来写脚本进行arp扫描,前面用的是shell脚本```sudo ./arp_disc.py eth0``` 用脚本的话要慢,首先这里设计的脚本不是多线程,其次还要判断超时的时间,当然为了准确性,scarp默认发两个数据包
> ```python
> #!/usr/bin/python
>
> import logging
> import subprocess
> logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
> from scapy.all import *
>
> if len(sys.argv) != 2:
> print "Usage - ./arp_disc.py [interface]"
> print "Example - ./ar_disc.py eth0"
> print "Example will perform an ARP scan of the local subnet to which eth0 is assigned"
> sys.exit()
>
> interface = str(sys.argv[1])
>
> ip = subprocess.check_output("ifconfig" + interface + " | grep 'inet' | cut -d'.' -f 1-3 | cut -d" " -f 10 | cut -d 'f' -f 1 ",shell = True).strip()
>
> prefix = ip.split('.')[0] + '.' + ip.split('.')[1] + '.' +ip.split('.')[2] + '.'
>
> for addr in range(1,254):
> answer = sr1(ARP(pdst=prefix+str(addr)),timeout = 1,verbose = 0)
> if answer == None:
> pass
> else:
> print prefix + str(addr)
>第二个脚本,这个脚本和arping的第二个脚本类似,都是可以调用已知的ip列表文件进行二层的发现:
./arp_disc.py ip_list.txt``` 脚本代码如下: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
> ```python
> #!/usr/bin/python
> #-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
>
> import logging
> import subprocess
> logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
> from scapy.all import *
>
> if len(sys.argv) != 2:
> print "Usage - ./arp_disc.py [filename]"
> print "Example - ./arp_disc.py ip_list.txt"
> print "Example will perform an ARP scan of the local subnet to which eth0 is assigned"
> sys.exit()
>
> filename = str(sys.argv[1])
> file = open(filename,'r') #打开文件列表
>
> for addr in file:
> answer = sr1(ARP(pdst=prefix+str(addr)),timeout = 0.1,verbose = 0) #verbose=0,不显示报错的具体信息
> if answer == None:
> pass
> else:
> print addr.strip() #将报错信息打印出来
>
总结:二层的发现主要是在拿下一台主机以后以此机器作为跳板进而对整个内网进行发现,但是由于内网的网络环境未知,而且服务器上面不一定有nmap,所以我们要利用一切可以利用的工具:arping,nmap,netdiscover,scopy等工具,以及自己编写的脚本
针对上面的两个脚本再补充两个多线程的脚本,就当做py练手了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52> #!/usr/bin/python
> # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
> import logging
> import subprocess
> import threading,time
>
> logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
> from scapy.all import *
>
> if len(sys.argv) != 2:
> print "Usage - ./arp_disc.py [interface]"
> print "Example - ./arp_disc.py eth0"
> print "Example will perform an ARP scan of the local subnet to which eth0 is assigned"
> sys.exit()
>
> interface = str(sys.argv[1])
>
> ip = subprocess.check_output(
> "ifconfig " + interface + " | grep 'inet' | cut -d'.' -f 1-3 | cut -d' ' -f 10 | cut -d 'f' -f 1 ",
> shell = True).strip()
> prefix = ip.split('.')[0] + '.' + ip.split('.')[1] + '.' + ip.split('.')[2] + '.'
>
>
> class MyThread(threading.Thread):
> def __init__(self):
> threading.Thread.__init__(self)
>
> def run(self):
> global answer,lock,n
> time.sleep(0.1)
> if lock.acquire():
> answer = sr1(ARP(pdst = prefix + str(n)),timeout = 1,verbose = 0)
> if answer == None:
> pass
> else:
> print prefix + str(n)
> n += 1
> lock.release()
>
>
> if __name__ == '__main__':
> n = 1
> ThreadList = []
> lock = threading.Lock()
> for addr in range(1,254):
> t = MyThread()
> ThreadList.append(t)
> for t in ThreadList:
> t.start()
> for t in ThreadList:
> t.join()
>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51> #!/usr/bin/python
> # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
> import logging
> import subprocess
> import threading,time
>
> logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
> from scapy.all import *
>
> if len(sys.argv) != 2:
> print "Usage - ./arp_disc.py [interface]"
> print "Example - ./arp_disc.py eth0"
> print "Example will perform an ARP scan of the local subnet to which eth0 is assigned"
> sys.exit()
>
> interface = str(sys.argv[1])
>
> ip = subprocess.check_output(
> "ifconfig " + interface + " | grep 'inet' | cut -d'.' -f 1-3 | cut -d' ' -f 10 | cut -d 'f' -f 1 ",
> shell = True).strip()
> prefix = ip.split('.')[0] + '.' + ip.split('.')[1] + '.' + ip.split('.')[2] + '.'
>
>
> class MyThread(threading.Thread):
> def __init__(self):
> threading.Thread.__init__(self)
>
> def run(self):
> global answer,lock
> time.sleep(0.1)
> if lock.acquire():
> for addr in range(1,254):
> answer = sr1(ARP(pdst = prefix + str(addr)),timeout = 1,verbose = 0)
> if answer == None:
> pass
> else:
> print prefix + str(addr)
> lock.release()
>
>
> if __name__ == '__main__':
> ThreadList = []
> lock = threading.Lock()
> for addr in range(1,200):
> t = MyThread()
> ThreadList.append(t)
> for t in ThreadList:
> t.start()
> for t in ThreadList:
> t.join()
>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49> #!/usr/bin/python
> # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
>
> import logging
> import subprocess
> import threading,time
>
> logging.getLogger("scapy.runtime").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
> from scapy.all import *
>
> if len(sys.argv) != 2:
> print "Usage - ./arp_disc.py [filename]"
> print "Example - ./arp_disc.py ip_list.txt"
> print "Example will perform an ARP scan of the local subnet to which eth0 is assigned"
> sys.exit()
>
> filename = str(sys.argv[1])
> file = open(filename,'r') # 打开文件列表
>
>
> class Mythread(threading.Thread):
> def __init__(self):
> threading.Thread.__init__(self)
>
> def run(self):
> global lock
> time.sleep(1)
> if lock.acquire():
> for addr in file:
> answer = sr1(ARP(pdst = addr.strip()),timeout = 0.1,
> verbose = 0) # verbose=0,不显示报错的具体信息,这里循环打开的是文件中的每一行IP地址
> if answer == None:
> pass
> else:
> print addr.strip() # 将报错信息打印出来
>
>
> if __name__ == '__main__':
> ThreadList = []
> lock = threading.Lock()
> for addr in range(1,200):
> t = MyThread()
> ThreadList.append(t)
> for t in ThreadList:
> t.start
> for t in ThreadList:
> t.join
>
>